
CONCEPTUAL ASPECTS OF UNIVERSITIES AND BUSINESS COOPERATION
Introduction. The importance of the higher education system for the development of society in any country is obvious. Today, universities both in Ukraine and abroad have many problems such as a low level of funding for higher education, a decrease in the number of students and applicants, obsolescence of the material fund, slow rates of integration into the European and world intellectual space, etc [7; 9]. One of the possible directions for their solution is the establishment of cooperation between higher educational institutions and businesses. Such cooperation can be beneficial to both parties.
Analysis of recent research and publications. Features of cooperation between business and universities are widely considered by scientists: O. Bercha [3], A. Oke [13], S. Tarasenko, T. Shcherbata [8], O. Yankovska, E. Pinto [11], G. Fernandes [11]. In general, the concept of university-businesses cooperation includes all systematic activities that, combine university and industry facilities and attempt to perform tasks that each of these two institutions cannot perform separately. Lin [9] considers the goal of cooperative relations between the university and business to be access to technology, the expansion of financial resources, and the use of innovative capabilities of universities. Kucherenko S. [5] and Pinto E. [11] also believe that businesses should establish relationships with other organizations that produce knowledge, such as universities, research and development centers, and others to develop innovative activities.
Materials and methods. The research methodology is based on the principles of structural and functional analysis of the cooperation processes between universities and businesses, comparative analysis, and synthesis. The scientific novelty of the study is the systematization of forms of cooperation between businesses and universities. The model of perspective directions of their interaction is offered. The practical implications of the results are that they can be used in management decisions and activities to optimize the interaction of business, universities, and science. The partnership of universities and businesses based on the pooling of resources such as financial, material and technical, and personnel, is a requirement of the time, the purpose of which is the accelerated development of interaction participants, a positive impact on the development of the country as a whole [4].
Results of the research and their discussion. It should be noted that the potential for cooperation between higher education institutions and businesses is much greater. Such cooperation is useful both for higher education institutions and for business [2], and the areas of cooperation between higher education institutions and business can be diverse - from the creation of innovative products and individual training of students to conducting joint research with universities on topical issues [2]. However, there are many problems with such cooperation today.
Unlike Ukrainian educational institutions, which are not very active in cooperation with enterprises, the system of higher education in European countries, such as Germany and the United Kingdom, has a pronounced applied nature and practical orientation.
Compared to European universities, US higher education institutions have a number of differences. For the American type of higher education, it is more typical to involve business in the administration system, when representatives of the largest firms become developers of educational programs and courses.
Leading foreign universities in Australia, the United Kingdom, Germany, Sweden, Finland, and the United States has already implemented many successful projects for small and medium-sized enterprises, and developed specialized programs to attract students to interact with representatives of the business community.
One of the barriers to the development of partnerships between enterprises and universities is the low investment attractiveness of Ukraine. Since the main source of funding for innovation costs are the funds of enterprises 97%, limited access to finance has a critical impact on the development of innovation in business. This factor has a negative impact on the development of partnerships between enterprises and universities due to limited funding for joint projects and research.
The next important barrier to the development of partnerships between enterprises and universities is the state of education and science in Ukraine. Now it has increased attention to the higher education system and university performance.
In today's conditions, innovative and information technologies are popular, and cooperation with higher education institutions is especially important for enterprises. Thus, the issue of developing effective partnerships between universities and enterprises is becoming increasingly important, which should be based on an individual approach to choosing a partner, an effective diagnosis of the partnership, and the optimal choice of strategy for the development of relationships.
It should be noted that the volume of expenses for the scientific research performance of Ukraine at the expense of all sources in 2020 was 16773.7 million UAH, including the expense of means of the state budget – 6020.9 million UAH which makes 35.89 %.
In the structure of domestic customer funds, the largest part was the funds of business sector organizations. Sources of financing of internal expenses for the performance of scientific and scientific and technical works in Ukraine in 2020 are given in fig. 1 [1, p.11].
.jpg)
In general, the share of expenditures on research and development in Ukraine is 0.47% of GDP, including 0.17 percent from the state budget. For comparison, in Sweden - 3.40%, Austria - 3.19%, Denmark - 2.96%, Germany - 3.18%, Finland - 2.79%, Belgium - 2.58%, France – 2.19%. As mentioned above, the costs of scientific work in Ukraine are financed, as a rule, at the expense of entrepreneurs and the state.
In Ukraine, there is also a tendency to reduce the performance of scientific and scientific-technical work by scientific institutions and universities. Figure 2 shows the dynamics of science intensity of Ukrainian GDP, %.
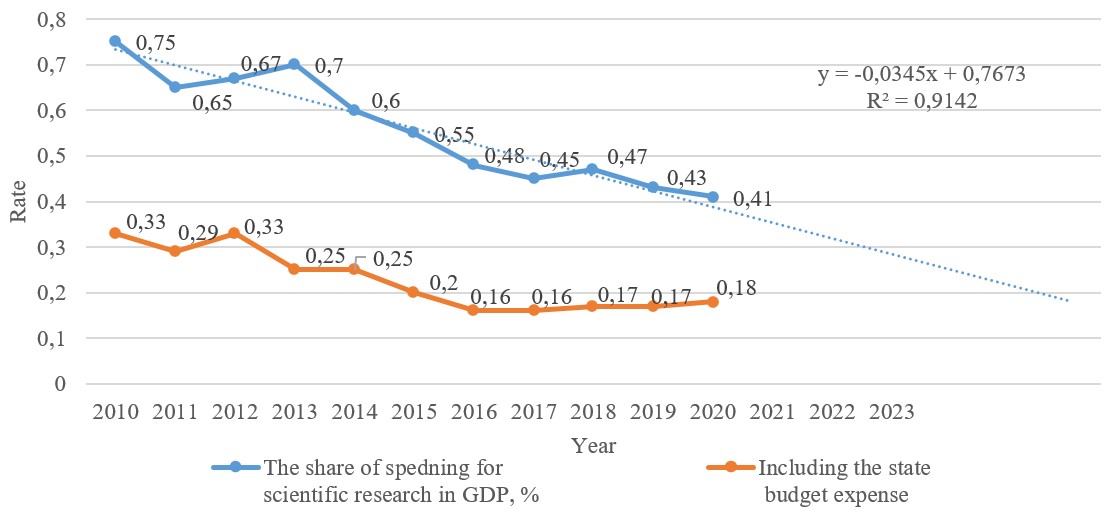
Therefore, the domestic scientific intensity of GDP is five times less than the average value of this indicator for EU countries. That is, Ukraine can compete only with countries that are not suppliers of new technologies or products with a high degree of added value.
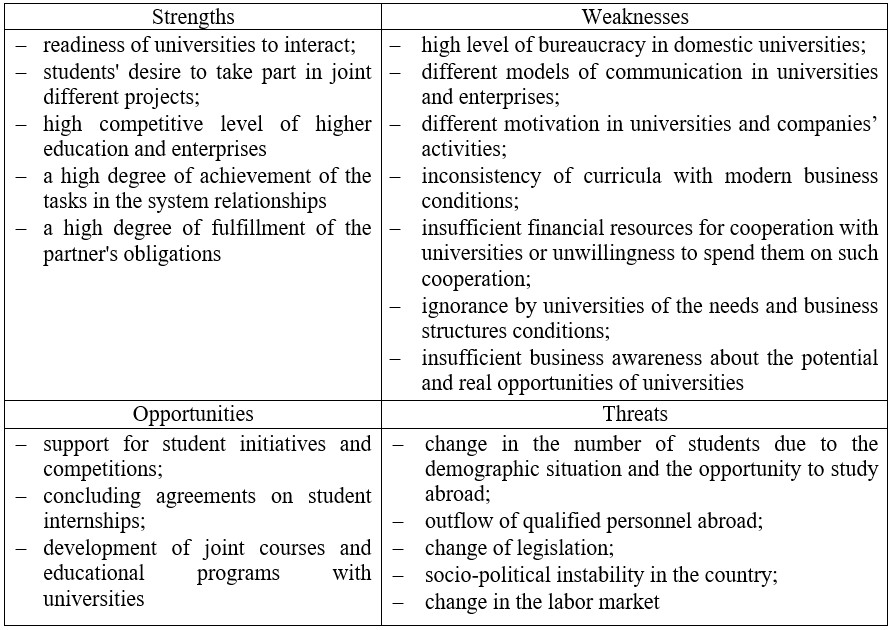
In order to determine further areas of effective development of partnership between businesses and universities, a SWOT analysis was used (table 1). Thus, the strengths of partnership and potential opportunities contribute to the strategy of growth of active activities and the development of new forms of cooperation.
In turn, weaknesses and threats reproduce the need for dialogue with partners in order to jointly seek opportunities to develop these relations.
The conducted SWOT analysis allows considering various variants of strategic decisions on the development of interaction between enterprises and universities.
Summarizing the most common definitions of partnerships in an enterprise by scientists, we highlight the following characteristic features [4; 7]:
- unity in a certain system of values and a separate environment;
- limited decision-making;
- synergistic effect of the result obtained and focus on the overall further development;
- flexibility to change and adaptability;
- interactivity, based on constant interaction and exchange of information, material, non-material resources, and business activity;
- interest in investment, innovation, and marketing activities.
 It should be noted that the most effective forms for the development of the system of interaction between universities and business are:
It should be noted that the most effective forms for the development of the system of interaction between universities and business are:
- involvement of companies for the joint effective development of curricula, which will take into account the requirements of employers to graduates of educational institutions. This guarantees successful employment for university graduates;
- monitoring by universities of new innovative technologies and trends in relevant areas of interest to employers;
- development of the distance education system;
- increasing the mobility of scientists to gain useful experience;
- effective development of the dialogue of universities with employers in order to increase mutual trust, and improve mutual understanding in formulating the goals of their activities.
It should be noted, that an important area of establishing partnerships between business and the university is to conduct all types of student internships on the basis of enterprises, which involves the implementation of the chain: educational practice - industrial practice - undergraduate practice - employment in the enterprise.
The study allowed proposing a model of cooperation between business and universities, which promotes the active use of the scientific and technical potential of universities, in modern conditions in Ukraine can be carried out in different ways (fig. 3).
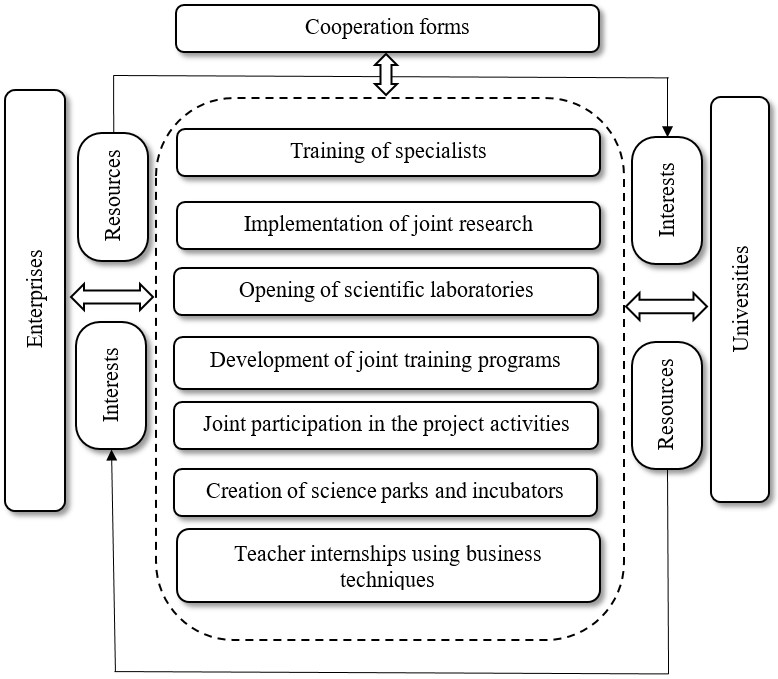
Thus, the formation and development of cooperation between universities and business provide, in our opinion, a real opportunity to form an optimal model of partnership, which is not only one of the competitive advantages of the university but also a necessary factor for its survival in the face of growing threats and challenges.
Conclusions and future perspectives of the study. Forms and areas of cooperation between universities and business structures, which can be useful to both parties, are diverse. Nevertheless, today there are significant barriers to organizing such cooperation. Strategic cooperation between employers and universities helps to jointly solve the problem of the lack of qualified specialists and the employment of graduates. In addition, an educational institution can give the business access to its infrastructure, help with research, or become a client of the company.
References
- The state of development of science and technology, the results of scientific and scientific and technical activities in 2020: analytical reference, Kyiv, 2021. URL: https://mon.gov.ua/storage/app/media/nauka/2021/06/23/AZ.nauka.innovatsiyi.2020-29.06.2021.pdf.
- Didyk A., Pogorelov Yu. Cooperation between the institution of higher education and business: principles of organization. Lviv Polytechnic National University Institutional Repository. 2018. pp. 75-84.
- Bertha O. Cooperation of universities and business as a basis of innovative development at the regional level. Scientific Bulletin of Uzhhorod University, 2017. pp. 110–115.
- Kutuzov V., Belash O., Muravyov A., Popov M., Ryzhov N., etc. Tools of strategic partnership of universities and enterprises, 2015.
- Kucherenko S. Current state, tendencies, and problems of education development in Ukraine. Economic Bulletin of Pereyaslav-Khmelnytsky State Pedagogical University named after Hryhoriy Skovoroda, 2018. pp. 51–58.
- Nemeschuk G. The effectiveness of higher education institutions in strategic partnerships with business. The strategy of economic development of Ukraine, 2013. № 33, pp. 265–270.
- Popravka I. Business cooperation with universities: opportunities for both parties. Personnel management. 2014. № 2. pp. 28–29.
- Shcherbata T.S. Development of partnerships of enterprises with higher educational institutions. Lviv. 2017. 211 p.
- Lin, J.Y. Alancing industry collaboration and academic innovation: The contingent role of collaboration specific attributes. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, № 123, pp. 216–228.
- Freire J.A.F., Gonçalves E. Cooperation in Innovative Efforts: a Systematic Literature Review. J Knowl Econ. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00837-3
- Pinto, E. B., & Fernandes, G. Collaborative R&D the key cooperation domain for university-industry partnerships sustainability –Position paper. Procedia Computer Science, 2021. № 181, pp. 102–109.
- Neves A. R. Costa J. Reis J. Using a Systematic Literature Review to Build a Framework for University-Industry Linkages using Open Innovation. Procedia Computer Science, 2021. №181, pp. 23–33. 10.1016/j.procs.2021.01.095.
- Oke A. Fernandes F. A. P. Innovations in Teaching and Learning: Exploring the Perceptions of the Education Sector on the 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR). Journal of Open Innovation, 2020. № 6(2), 31. Advance online publication. 10.3390/joitmc6020031.
- Nam G.M., Kim D.G., Choi S.O. How resources of universities influence industry cooperation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 2019. Volume 5, Issue 1. https://www.mdpi.com/2199-8531/5/1/9.
- Laine, K.; Leino, M.; Pulkkinen, P. Open innovation between higher education and industry. J. Knowl. Econ, 2015, №6, pp. 589–610.
